
The Danger of Dependency
Imagine this: you’ve just launched your SAP system, and everything seems to be running smoothly. But behind the scenes, the system relies on a select few individuals who were instrumental in the implementation process. While their expertise was invaluable during the project, leaning too heavily on them especially for the long term can spell trouble.
From operational disruptions when personnel are unavailable to knowledge silos hindering innovation to hefty incurred expenses, reliance on key personnel can have far-reaching consequences. Below are some common ways businesses find themselves in this situation, and how to address those pitfalls:
Resistance to Change: Resistance to change can pose a significant barrier to reducing dependency on key personnel during SAP implementation. In particular, employees may be comfortable with existing processes and hesitate to embrace new technologies or workflows. This resistance can manifest in various forms, such as skepticism, fear of the unknown, or reluctance to disrupt established routines. To overcome resistance and foster a culture of adaptability, organizations can employ several strategies:
Education and Awareness: Provide comprehensive education and training programs to help employees understand the benefits of the changes. Highlight how the new processes or technologies will improve efficiency, streamline operations, and support long-term growth.
Communication and Transparency: Foster open and transparent communication channels to address concerns and dispel misconceptions. Engage employees in discussions about the reasons behind the changes, the expected outcomes, and how their roles may evolve. Encourage feedback, and actively listen to employees’ perspectives to address their apprehensions effectively.
Leadership Support and Role Modeling: Secure buy-in from senior leaders and managers who play influential roles in driving organizational change. Leaders should demonstrate their commitment to the changes by actively participating in training sessions, embracing new technologies themselves, and championing the benefits of adaptation.
Incentives and Recognition: Offer incentives or rewards to motivate employees to embrace change and participate in training initiatives. Recognize and celebrate early adopters and success stories to inspire others and reinforce the importance of adaptability.
Continuous Support and Reinforcement: Provide ongoing support and resources to employees throughout the transition period. Offer refresher training sessions, access to support materials, and opportunities for skill development to ensure sustained adoption of new processes and technologies.

Tailor Communication to Stakeholder Needs: Customize communication strategies to resonate with different stakeholder groups. Executives may require high-level overviews of the benefits and strategic implications, while frontline employees may need detailed information about how the changes will impact their day-to-day responsibilities.
Build Relationships and Trust: Invest time and effort in building relationships with stakeholders and earning their trust. Engage in regular dialogue, seek input and feedback, and demonstrate a genuine interest in addressing their concerns and priorities.
Create a Compelling Vision: Articulate a clear and compelling vision for the future state of the organization. Emphasize how reducing dependency on key personnel aligns with strategic objectives. Illustrate the benefits of collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation that can result from embracing change.
Empower Stakeholder Participation: Encourage stakeholder participation and involvement in decision-making processes related to the changes. Provide opportunities for stakeholders to contribute ideas, shape implementation plans, and take ownership of initiatives aimed at reducing dependency.
Monitor Progress and Adjust Approach: Continuously monitor stakeholder engagement and feedback to assess the effectiveness of communication and engagement efforts. Be prepared to adjust the approach based on evolving needs and concerns to maintain stakeholder buy-in throughout the change process.

Prioritize Training Needs: Conduct a thorough assessment of training needs and prioritize areas where skill development is most critical for reducing dependency on key personnel. Focus on essential competencies required to operate and maintain SAP systems effectively.
Leverage Internal Expertise: Identify internal subject matter experts who can serve as trainers or mentors to facilitate knowledge transfer and skill development. Tap into existing talent within the organization to deliver training sessions, lead workshops, and provide on-the-job coaching.
Explore Cost-Effective Training Solutions: Look for cost-effective training solutions, such as online courses, virtual training platforms, or self-paced learning modules. These options offer flexibility and scalability while minimizing the financial burden associated with traditional classroom-based training.
Seek External Support and Partnerships: Explore partnerships with external training providers, consulting firms, or industry associations that offer expertise in SAP systems and related technologies. Collaborate with these organizations to access specialized training programs, workshops, and certification opportunities.
Foster a Learning Culture: Cultivate a culture of continuous learning and development within the organization by promoting the value of ongoing skill enhancement. Encourage employees to take ownership of their professional development, and provide support for pursuing relevant certifications, attending conferences, or participating in industry events.
Overall, the best way for businesses to combat this issue is through building resilience in their system and workforce. By addressing resistance to change, gaining buy-in from stakeholders, and overcoming resource constraints for training and development, organizations can effectively reduce dependency on key personnel.
User Adoption Strategies
A successful user adoption is one of the best ways to avoid reliance on key personnel. Below are a few of the core User Adoption Strategies businesses should keep in mind:
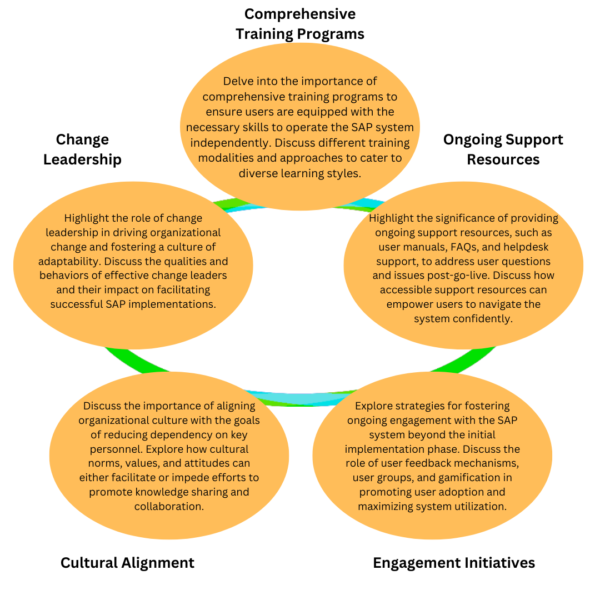
Communication Strategies
While working to ensure successful user adoption, keep the following communication strategies in mind:
Effective Change Communication: Provide tips and best practices for communicating changes effectively to employees and stakeholders. Emphasize the importance of transparency, clarity, and empathy in addressing concerns and managing expectations.
Promoting Collaboration: Explore strategies for promoting collaboration among team members to facilitate knowledge sharing and reduce dependency on individual expertise. Discuss the role of communication channels and platforms in fostering collaboration and information exchange.
 Additional Strategies for Resilience
Additional Strategies for Resilience
Businesses can benefit from other preventative measures and best practices to avoid reliance on key personnel. Here are some proactive strategies to ensure resilience and continuity in your SAP operations:
Knowledge Transfer and Documentation: Don’t let valuable insights reside solely in the minds of a few individuals. Document processes, procedures, and best practices, and conduct knowledge transfer sessions to share expertise across the organization.
Example: Host interactive workshops where experienced team members share their knowledge and insights with others. Encourage active participation and create comprehensive documentation that serves as a valuable resource for all team members.
Cross-Training and Skill Development: Build redundancy by identifying successors for key roles and investing in cross-training programs. By equipping multiple team members with the necessary skills, you’ll ensure that critical tasks can be performed even in the absence of key personnel.
Example: Implement a mentorship program where seasoned employees mentor junior staff members. Encourage cross-functional collaboration and provide opportunities for employees to gain hands-on experience in different areas of SAP operations.
Implementing Redundancy Measures: Establish backup roles and succession plans to mitigate the risk of dependency on specific individuals. Cross-functional teams, job rotation programs, and succession planning initiatives can ensure continuity in the face of turnover or unavailability.
Example: Create a detailed succession plan that identifies potential successors for key roles within the organization. Regularly review and update the plan to reflect changes in personnel and organizational needs.
Leveraging Technology Solutions: Harness the power of technology to reduce reliance on individual expertise. Knowledge management systems can capture, organize, and share knowledge effectively across the organization, while automation tools streamline repetitive tasks to ensure consistent performance and efficiency.
Example: Implement a centralized knowledge management platform where employees can access information, documents, and best practices related to SAP operations. Integrate automation tools to streamline routine tasks and minimize the impact of staff turnover on day-to-day operations.
 Post-Go-Live Monitoring and Evaluation
Post-Go-Live Monitoring and Evaluation
The journey doesn’t end once you’ve implemented these strategies. You must continually monitor and evaluate their effectiveness to avoid reliance on key personnel long term:
Regular Performance Reviews: Assess the effectiveness of your strategies through regular performance reviews. Recognize achievements, address challenges, and adapt your approach based on feedback to ensure ongoing success.
Example: Conduct quarterly performance reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented strategies and identify areas for improvement. Solicit feedback from employees and stakeholders to gain insights into their experiences and perspectives.
Assessing Knowledge Retention: Gauge the extent to which critical knowledge has been transferred and retained within the organization. Identify areas for improvement, and take corrective action as needed to strengthen knowledge retention efforts.
Example: Administer knowledge retention assessments to measure employees’ understanding and proficiency in key areas of SAP operations. Use the results to identify gaps and develop targeted training programs to address knowledge retention challenges.
Adjusting Strategies as Needed: Stay agile, and be prepared to adjust your strategies based on feedback and evolving risks. After all, flexibility is key to navigating the ever-changing landscape of SAP implementation and ensuring long-term success.
Example: Monitor market trends and technological advancements to anticipate changes that may impact SAP operations. Continuously review and refine your strategies to align with evolving business needs and industry standards.
SAP Post-Implementation General Management
Below are a few findings from SAP, SAPMint, and TechTarget that discuss how to manage post-implementation. This proper management is vital to avoiding long-term dependence on key personnel.
 The Value of Post-Implementation Support
The Value of Post-Implementation Support
Businesses need to recognize the importance of post-implementation support, so they can optimize system performance and reduce reliance on specific personnel.1 In particular, post-implementation support offers continuous system optimization, opportunity to assess any errors or bugs, opportunity to keep on top of updates, and expert guidance, maximizing the value of SAP investment. To aid in this process, businesses should understand the different support services available and select the right support provider to maintain system stability and achieve desired outcomes.
To make the most of post-implementation support, businesses should focus on regular system health checks, comprehensive user training, and management of new features and enhancements. These efforts ensure optimal system performance, driving business growth and success (and avoiding reliance on key personnel).
Tips for Post Go-Live2
- Addressing Incidents: Be the first line of defense when end-users encounter issues. From attempting resolutions to escalating to SAP Support if necessary, prompt action is key to maintaining operational efficiency.
- Managing User Access: Ensure that user access authorizations are up-to-date, handle substitutions, and keep an eye on monitoring business tasks to prevent any disruptions.
- Supervising Background Jobs: Monitor background jobs, and facilitate seamless communication with external systems to ensure data integrity and smooth operations.
- Adapting the Solution: Stay agile by adjusting the solution as required. This may involve modifying form templates, adjusting scope, and tweaking configuration settings to align with evolving business needs.
- Conducting Upgrades and Testing: Keep your SAP system up-to-date by conducting upgrades and testing new features. Stay ahead of the curve by exploring the latest advancements and ensuring your system is optimized for peak performance.
If you opt for this system, below are a few best approaches to keep in mind:
- Notification Process: Customers receive email notifications from SAP approximately 4-6 weeks prior to the production tenant upgrade. Ensure that communications are directed to the designated IT contact listed in the Service Control Center.
- Accessing Release Notes: Businesses can stay updated with the latest enhancements and fixes by accessing release notes in the Help Center documentation under “What’s New.”
- Testing Process: The test tenant undergoes an upgrade two weeks before the production upgrade. While upgrades are positioned as routine occurrences, businesses need to observe precautions during this period to avoid any disruptions.
- Precautionary Measures: During the two-week period following the test tenant upgrade, avoid merging change projects, undergoing go-lives, or applying partner solutions through the SAP Cloud Applications Studio.
- Restore Points: Previously requested restore points will not be accessible after the upgrade. Plan accordingly and ensure data backup measures are in place.
Additional Go-Live Tips to Keep in Mind3

At the end of the day, businesses need to avoid dependency on former key personnel to ensure the success and sustainability of SAP implementations. By implementing proactive strategies and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can navigate the post-go-live phase with confidence, safeguarding their SAP systems and positioning themselves for long-term success in the ever-evolving world of SAP implementation.
1 Navigating Challenges: How SAP Post-Implementation Support Empowers Businesses (sapmint.com)
2 “After Go-Live.” https://learning.sap.com/learning-journey/sap-sales-and-service-cloud-administration/after-go-live_f5f8f0e5-1923-4335-8bb9-0bac0f51353c
3 “10 Steps You Need to Carry Out Post-ERP Implementation.” https://www.techtarget.com/searchERP/tip/10-steps-you-need-to-carry-out-post-ERP-implementation

 Additional Strategies for Resilience
Additional Strategies for Resilience Post-Go-Live Monitoring and Evaluation
Post-Go-Live Monitoring and Evaluation The Value of Post-Implementation Support
The Value of Post-Implementation Support


